Site Alliances: Breaking Through Operators' MBB Development Obstacles and Driving Rapid and Sustained MBB Growth in the South Pacific
What Can Be Done to Achieve Structural Growth in the South Pacific Market?
As the MBB industry develops, the growth in the number of connections in the South Pacific market is expected to follow a highly similar exponential growth pattern. Network capabilities depend on spectrum, site quantity, RAT, multi-channel, multi-sector, and other technologies. With insufficient spectrum resources and slow spectrum release, current sites and technologies can only support 58% of network services in mainstream South Pacific markets. New sites must be built to support remaining 42% of services. Doubling the number of sites is the only route for mainstream operators in the region to sustain growth, with both sites and spectrum providing to be the most valuable resources.
The two-fold increase in the number of sites is aimed to accelerate B2B service deployment and achieve structural growth. Operators in the South Pacific consider this action to be as an entrance strategy with the following agendas:
1.The South Pacific market can be divided into the three major markets of Indonesia, the Philippines, and Malaysia. These markets feature the lowest recorded site density in the world (low in comparison to developing countries), hindering service development and sustainable growth. It is estimated that every 1 million users in the Philippines share 68 sites. Major operators in Indonesia deploy on average 100 sites for every 1 million users, and the site density in Malaysia is lower than 300 sites per million users.
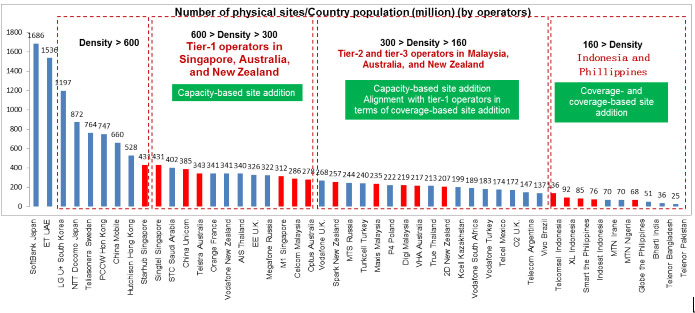
2.An analysis of available site resources in these three countries shows that besides traditional towers, there are a large amount of idle sunk resources, such as utility and lamp poles. For example, 530 thousand utility and lamp poles in Indonesia, more than 70 thousand in the Philippines, and more than 60 thousand in Malaysia. These countries also consist of thousands of chain supermarkets and more than 4000 large buildings, which are all valuable potential site resources.

3.Huawei has sought to help customers deploy networks, but the site deployment progress is still relatively slow (for example, only 98 sites in the Philippines were delivered in 2015). Why? The reason is that stakeholders in the profit chain do not truly understand where the value lies. Stakeholders only focus on a small number of properties and sites and current benefits, but know little about future industry development, value, and prospective issues.
So what can be done to resolve this structural problem? The Southern Pacific Region opted to tackle this challenge by setting up large site industry alliances.
How Are Site Industry Alliances Positioned and What Is the Essence of Such Alliances?
From the perspective of the industry chain, the traditional industry chain is an open system. Industry players tend to compete with each other instead of joining forces to enjoy mutual collaborative benefits. The traditional method cannot efficiently resolve current issues. Therefore, the Southern Pacific Region comprehensively re-examined the whole industry chain after determining the strategy and leveraged Huawei advantages to discover new valued opportunities. These actions helped to effectively stimulate the industry chain to create new value based on characteristics and requirements of industry chain stakeholders. In addition, different parties in the value chain are divided into two loops and industry alliance-based operation is performed to create a harmonious ecosystem. Loop 1 focuses on scale and share, and loop 2 focuses on new business opportunities and new blue oceans. Industry alliances proved ultimately beneficial in facilitating an industry chain transformation from open to closed loop mode. Previously opted to engage in high-profile actions, industry alliances now focus on pragmatic and practical efforts to provide better results.
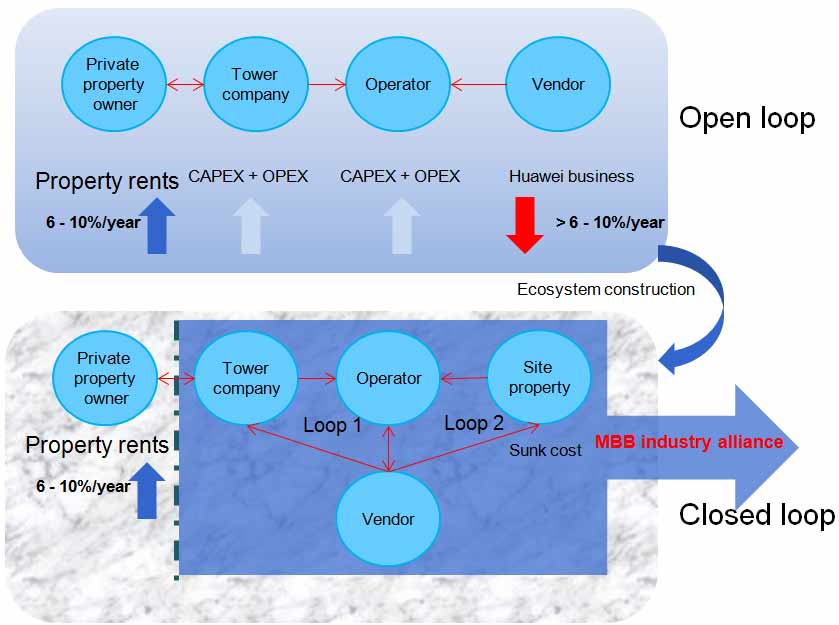
Two essences of industry alliances:
1.Industry alliances enable industry players to understand industry development, trends, and the current and future value and prospective issues.
2.As the sponsor, Huawei will inspire the industry chain to create newly added value, achieving mutual benefits and win-win cooperation.
Role of Huawei in Industry Alliances
What qualifies Huawei as the alliance sponsor to inspire the industry chain to create newly added value?
Huawei enjoys the inherent benefits of massive scale and market share in the South Pacific market. Huawei's market awareness and substantial abundant knowledge of deployed networks, vacant sites, and available potential locations (sites that can be rented to multiple operators) help to maximize industry chain value.
Huawei demonstrates sponsorship competency equipped with a powerful platform, network insight, BNC, quick response capabilities, scenario-based solutions, and efficiently accurate tool supporting platforms.
Huawei is able to spur joint innovation in the industry chain and discover new revenue blue oceans through capability exposure to expand market share.
New Value of the Business Model Adopted By Site Industry Alliances
Establishing site industry alliances means significantly more than simply organizing a large group of individuals. Where is the future value? Should we adapt to the evolving trend of Internet development? What is the value of data traffic? These are questions that such alliances are required to answer. Site industry alliances must help realize the vision of all industry chain members to derive valuable contributions.
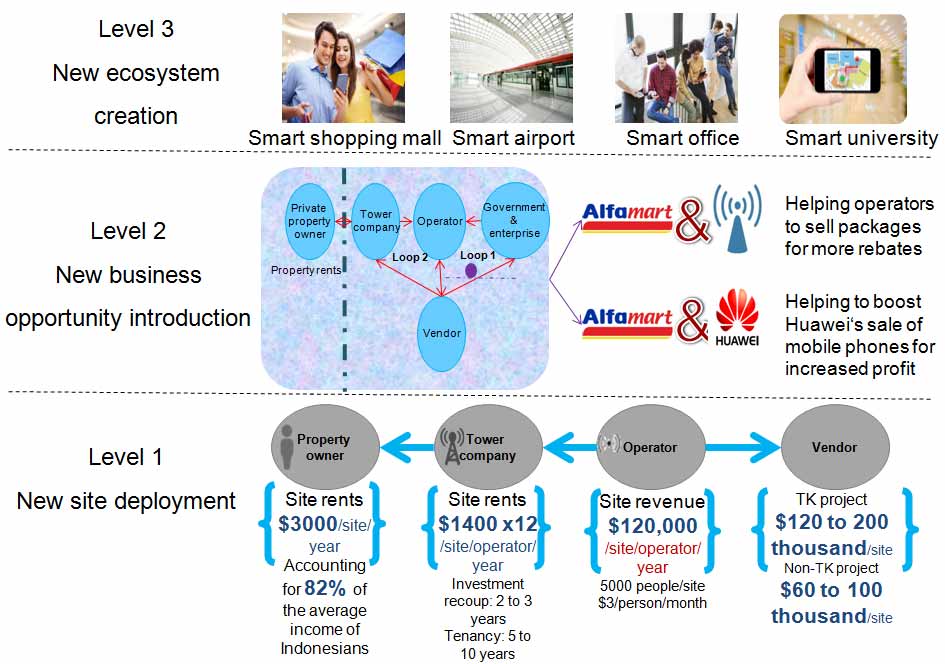
1.Traditional tower companies: Sites can also produce market share advantages. Cooperation with Huawei helps tower companies quickly perform large-scale deployment of sites to gain scale and share advantages, transitioning from passive to proactive site deployment.
2.Properties/large chain supermarkets:
1) Use current resources to earn new rents and service revenue.
2) Use new business opportunities (sell smart terminals and operator packages) to provide new revenue.
3) Indoor property groups: Besides traditional renting services, Huawei's indoor solution provides a standard API for vertical industry services. Huawei also co-develops vertical industry services and applications on the industry chain exposure platform. This joint innovation can create new revenue for property owners, app developers, and operators, while also providing mutual value shared benefits.
3.Governments: Activate sunk public resources by increasing the usage of public resources such as lamp poles, utility poles, bus stations, public service advertisement boards to create additional social value.
4.Operators:
1) Transform site acquisition methods from single to one-off batch acquisition for quick network deployment.
2) Negotiate site resources in batches to greatly provide lower rent and improve ROI.
3) Leverage properties of large chain supermarkets and perform batch application to minimize time-consuming permit application processes for agile site deployment.
New Progresses on Site Industry Alliances
Indonesia: Using the industry alliance, operators in the country have signed with AlfaMart, IndoMart, and IndoMobile for site resources at more than 25,000 chain supermarkets. Operators have also signed with the MAC property company for indoor site resources at 750 large buildings. Significant efforts are being made to filter out available site locations from obtained site resources, with the discovery of more than 3800 valued site locations.
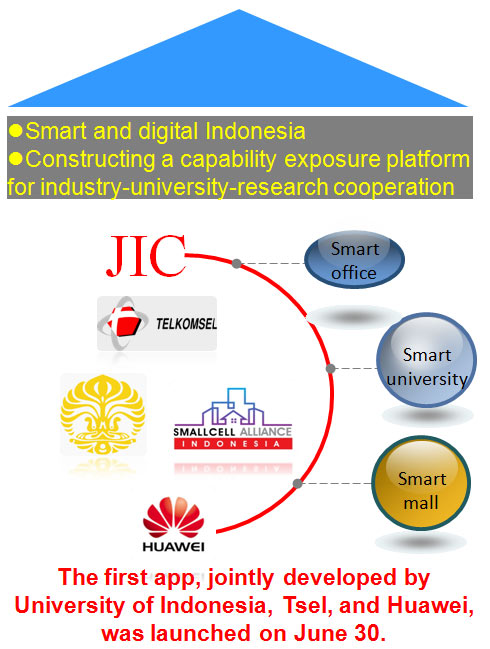
Huawei joined hands with JIC, a joint innovation platform, to hold the best app competition for students at the University of Indonesia. The first app jointly developed by Huawei, Tsel, and the University of Indonesia, was launched, driving SVA deployment and the introduction of training sessions in China for Indonesian students.

The Philippines: Approximately 2510 friendly site locations have been obtained from FTK, among which 1129 are suitable for macro sites. Up to 336 POs have been obtained. To deploy sites in multiple scenarios, the Philippines Rep Office designed, verified, and delivered a multi-scenario agile site deployment solution, which includes the lamp pole-mounting solution for business areas, MRT/LRT transportation hub solution, and MSAN/Blade integration solution. As batch site acquisition and filtering are currently applied, these solutions will soon be deployed on a large scale.
Malaysia: U Mobile cooperates with MITCH, a tower company in Malacca, on site acquisition and has obtained 24 towers for site deployment, ending the situation that U Mobile had no self-operated sites in Malacca.
NAZA has signed to provide utility pole resources, specifically 30 lamp poles for Webe and 19 for Celcom. Webe and Celcom also work with NAZA to install, test, and verify lamp pole-mounting site devices, laying a solid foundation for follow-up large-scale commercial deployment.
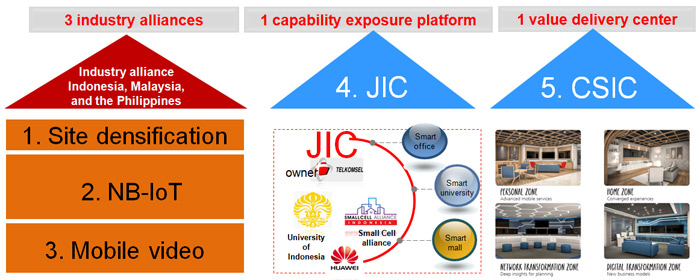
MBB Ecosystem Construction in South Pacific
A range of MBB industry alliances are established in the South Pacific to ensure that operators will not encounter structural declines and can double the amount of growth. These alliances include three new areas of focus — site densification, NB-IoT, and mobile video, aimed towards increasing the number of sites at a specific location and consolidating basic wireless networks. Huawei joins with operators in the region and the University of Indonesia for collaborative innovation and construction of a capability exposure platform. Huawei also incorporates the use of the Three Clouds (CSIC platform) to ensure extensive and in-depth value delivery and enablement in the industry chain, helping to establish a harmonious ecosystem and further driving industry development.