Multi-Layer Networks: the Site Deployment Model of the MBB Era
Future Service Trends and Network Challenges
Applications emerging in today's MBB era are changing user behaviors and affecting operator strategies for network deployment. Huawei's practical experience and global research has identified three trends driven by future data service development and network evolution. First, users require a superior broadband experience (high signal level, video-sufficient capacity, and millisecond-level latency) on mobile networks. Second, diversified services require operators to plan and leverage spectrum and site resources in multi-RAT, multi-band, and multi-site hybrid HetNets for seamless experience. Third, 5G networks require more complex architecture and ultra-high density. Various market segments present high service requirements, which can be fulfilled by diversifying site forms.
Operators have concerns and challenges about network deployment. First, site acquisition is increasingly arduous. Most operators struggle to add macro sites over inter-site distances under 300 meters (or 600 meters in some countries). Second, macro sites no longer fulfill the network requirements of excellent experience services, particularly in indoor or spectrum-deficient scenarios. Third, boosting network capabilities by carrier or spectrum addition but without site addition cannot improve weak or discontinuous coverage and the cell edge experience in urban areas. Inadequate or fragmented coverage issues remain unresolved.
Therefore, MBB calls for deployment of networks that are layered and transformed from 2D to 3D. Deployment itself must transform from flood-style to targeted.
Multi-Layer Networks: Outside-In and Top-Down
Operators need to change their network planning and deployment philosophy . Macro sites alone are no longer enough. Multi-layer networks intensify coverage and absorb traffic, improving user experience, boosting network competitiveness, and driving 5G evolution.
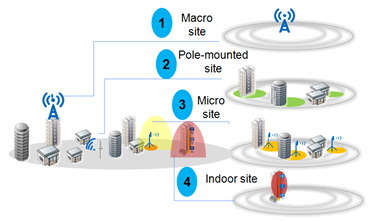
- First layer: wide, continuous, and shallow coverage provided by traditional macro sites fulfills basic coverage and capacity requirements
Operators often deploy macro sites at rooftops higher than 20 meters. The average distance between sites exceeds 300 meters due to site acquisition difficulties in urban areas. Continuous coverage provided by macro sites is the basic network layer and fulfills basic data service requirements.
- Second layer: quick, comprehensive, and intensive coverage provided by pole-mounted sites offloads hotspot traffic
Operators often deploy such sites on lamp, electricity, video surveillance, and billboard poles to resolve insufficient indoor coverage and hotspot capacity issues. These poles are 10 to 20 meters high, and sites deployed on them cover a radius of 100 to 200 meters. Pole-mounted sites have extra functions such as video surveillance, lighting, and alarm reporting. Such intelligent sites speed up site acquisition while creating new business models and increasing site revenue. Pole-mounted sites have been deployed on a large scale in densely populated cities such as Shanghai, China and Bangkok, Thailand.
- Third layer: intensive indoor coverage provided by outdoor micro sites offloads part of hotspot traffic
As with the second layer, the third layer fills coverage holes and provides extra hotspot coverage. This layer is suitable for densely inhabited residential areas. The Villa Radio solution is an example of targeted coverage thanks to one RHUB and multiple book RRUs. These outdoor micro sites are often deployed at heights of 5 to 10 meters for a coverage radius of 50 to 150 meters.
- Fourth layer: high-value intensive indoor coverage provided by indoor sites offloads outdoor site traffic
Airports, stations, stadiums, hotels, and office buildings are scenarios where service volume exceeds outdoor site capacity. Indoor sites help to cover these high-value areas and improve user experience.
The New Multi-Layer MBB Network Deployment Model
Multi-layer networks provide comprehensive, intensive coverage while absorbing traffic. Only then can u ser experience meet high MBB standards. Huawei partners with global operators to integrate resources and establish site ecosystems for quick site acquisition. Further innovation into site forms for high-value site deployment scenarios builds healthy markets and creates more value. Learn more about multi-layer networks at the Unleashing Site Potential Booth at MWC 2017.